Understanding BTU ratings is essential for commercial kitchen operators looking to optimize their equipment's performance and energy efficiency. BTU, or British Thermal Unit, is a measurement of the heat output of a piece of equipment. The higher the BTU rating, the more powerful the equipment is in terms of heating or cooling capabilities. By knowing and comparing BTU ratings, businesses can make informed decisions when selecting restaurant equipment that meets their specific needs and budget constraints.
What Is a BTU?

BTU, or British Thermal Unit, is a standard measurement used to quantify the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. In the context of commercial equipment, BTU ratings indicate the heating or cooling capacity of appliances such as ranges, ovens, refrigerators, and air conditioning units. Understanding BTU ratings is crucial for selecting equipment that can efficiently meet the heating or cooling needs of a commercial kitchen or establishment.
Why Do BTUs Matter?
BTU ratings are crucial when selecting commercial kitchen equipment. Equipment with BTUs that are too high can lead to wasted energy and potential safety hazards. Equipment with BTUs that are too low may not be able to meet the demands of a busy kitchen, resulting in slower cooking times and decreased efficiency. It’s important to consider the optimal BTU rating for each piece of equipment to ensure optimal performance and energy conservation in a commercial kitchen setting.
BTUs and Recovery Time
One key aspect to consider is the equipment's BTU rating in relation to its recovery time. Recovery time refers to the ability of the equipment to regain its operating temperature after a sudden drop caused by adding cold ingredients or opening the door frequently. Equipment with higher BTU ratings generally has a faster recovery time. For example, a high-BTU range can quickly recover its temperature after searing a large batch of meat or boiling a large pot of water. This is essential in a busy commercial kitchen where efficiency is paramount.
Conversely, equipment with lower BTU ratings may have a slower recovery time, leading to longer wait times between batches or dishes. This can impact the overall productivity of your kitchen and result in slower service during peak hours. It's important to match the BTU rating of your equipment with the specific needs of your kitchen. For high-volume operations, investing in equipment with higher BTU ratings and faster recovery times can help maintain a smooth workflow and meet customer demand effectively.
Gas Range BTU

The BTU rating of a gas range is a crucial factor to consider when selecting the right equipment for your kitchen. BTU ratings indicate the amount of heat output a gas range can provide, influencing its cooking efficiency and performance.
Commercial gas ranges typically have BTU ratings ranging from 20,000 to 60,000 BTUs per burner. Higher BTU ratings mean the burners can generate more heat, allowing for faster cooking times and the ability to handle large quantities of food. This is particularly beneficial for busy kitchens that need to prepare meals quickly and efficiently.
When choosing a gas range for your commercial kitchen, it's important to consider the type of cooking you will be doing. For high-volume cooking or tasks that require rapid heating, such as stir-frying or searing, a gas range with higher BTU ratings between 20,000 and 60,0000 is recommended. On the other hand, if you mainly do light cooking or simmering, a lower BTU rating between 10,000 and 20,000 may suffice.
How to Calculate Total BTU for Gas Range

To determine the total BTU output of the range, simply add up the BTU ratings of each burner. For example, a gas range with four burners each rated at 30,000 BTUs will have a total output of 120,000 BTUs. This higher total BTU output can be beneficial for cooking multiple dishes simultaneously or for handling large pots and pans.
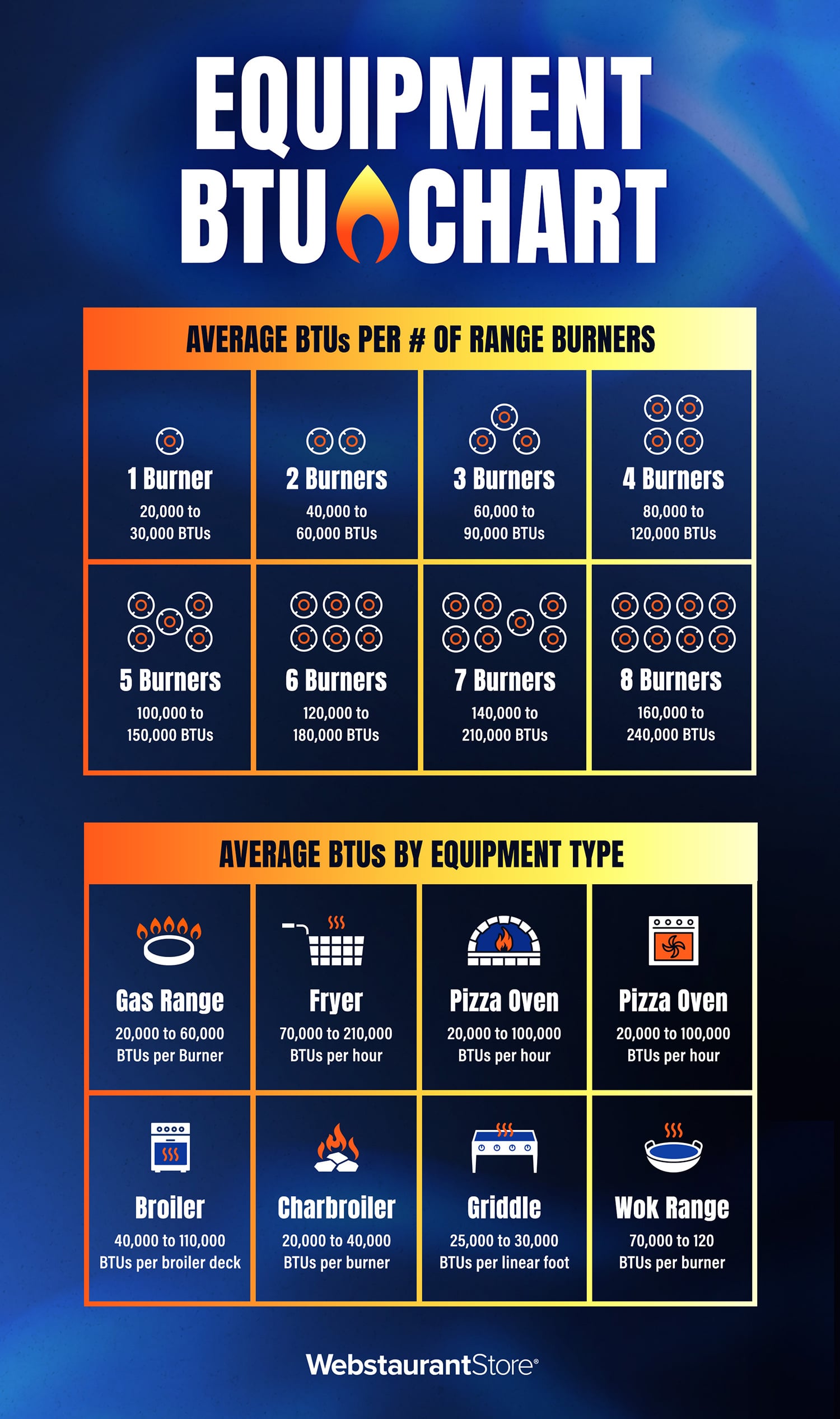
- 1 Burner - 20,000 to 30,000 BTUs
- 2 Burners - 40,000 to 60,000 BTUs
- 3 Burners - 60,000 to 90,000 BTUs
- 4 Burners - 80,000 to 120,000 BTUs
- 5 Burners - 100,000 to 150,000 BTUs
- 6 Burners - 120,000 to 180,000 BTUs
- 7 Burners - 140,000 to 210,000 BTUs
- 8 Burners - 160,000 to 240,000 BTUs
Equipment BTU Ranges
Below, we cover the most common kitchen equipment and their BTU ranges to help you choose the best products for your business.
- Gas Range: 20,000 to 60,000 BTUs per burner
- Fryer: 70,000 to 210,000 BTUs per hour
- Pizza Oven: 20,000 to 100,000 BTUs per hour
- Convection Oven: 40,000 to 50,000 BTUs per hour
- Broiler: 40,000 to 110,000 BTUs per broiler deck
- Charbroiler: 20,000 to 40,000 BTUs per burner
- Griddle: 25,000 to 30,000 BTUs per linear foot
- Wok Range: 70,000 to 120,000 BTUs per burner
BTU Hood Requirements
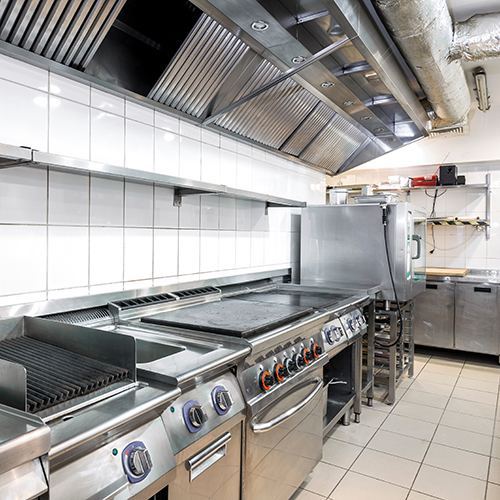

In addition to selecting the right equipment for your kitchen's needs, it's essential to consider how the BTU output of your appliances impacts hood requirements. The BTU rating of a piece of equipment determines the size and capacity of the ventilation hood needed to effectively remove heat, smoke, and grease from the cooking area.
For gas-powered equipment, the higher the BTU output, the more heat is generated during operation. This means that high-BTU appliances like ranges, griddles, and fryers require larger hoods with higher exhaust rates to effectively capture and remove the excess heat and grease produced during cooking.
Commercial kitchens are required to comply with local building and fire codes, which often specify the minimum exhaust rates and hood sizes based on the total BTU output of the cooking equipment in use. Failure to meet these requirements can lead to poor indoor air quality, increased fire risk, and potential fines or penalties. To determine the appropriate hood requirements for your kitchen, calculate the total BTU output of all gas-powered equipment that will be in use simultaneously. This information can help you select the right hood size, exhaust rate, and filtration system to maintain a safe and comfortable working environment for your staff.
BTU FAQs
Here are the answers to some of the most common BTU questions you may have:
BTU vs Watts
When comparing BTUs to watts in commercial equipment, it's important to understand the distinction between the two units of measurement. BTUs (British Thermal Units) measure the amount of heat generated or removed, while watts measure the rate of energy consumption or production. In commercial settings, BTU ratings are commonly used to determine the heating or cooling capacity of equipment, such as ranges, griddles, and refrigeration units, while watts are often used to quantify the power consumption of electrical appliances. If you’re looking to compare the output of an electric unit compared to a gas unit, 1 watt is equal to 3.41 BTUs per hour.
Propane vs Natural Gas BTU Output
Most gas-powered equipment will be available in either natural gas or propane. These gas types have different BTU capabilities. Propane contains about 2,516 BTUs per cubic foot, while natural gas contains around 1,030 BTUs per cubic foot. This means that propane has a higher energy content and can generate more heat per unit volume compared to natural gas. When selecting equipment that uses either propane or natural gas, it is crucial to consider the BTU ratings to ensure optimal performance.
BTU Chart
Use this helpful BTU chart to understand the BTU outputs of your kitchen appliances:
By knowing the BTU output of your appliances, you can ensure efficient operation in your commercial kitchen. Higher BTU ratings indicate more powerful equipment, suitable for high-volume cooking, while lower BTU ratings are ideal for smaller operations. Keep in mind the specific needs of your kitchen when comparing BTU ratings to make informed decisions that will benefit your business in the long run.