To ensure the safety and quality of food, chefs must know the minimum internal cooking temperatures of different dishes. Cooking food to the right temperature enhances its taste and texture and eliminates harmful pathogens that can cause foodborne illnesses. Whether you're a professional chef or a culinary student, learning the recommended cooking temperatures is essential for maintaining food safety standards and avoiding the temperature danger zone.
Safe Cooking Temperatures
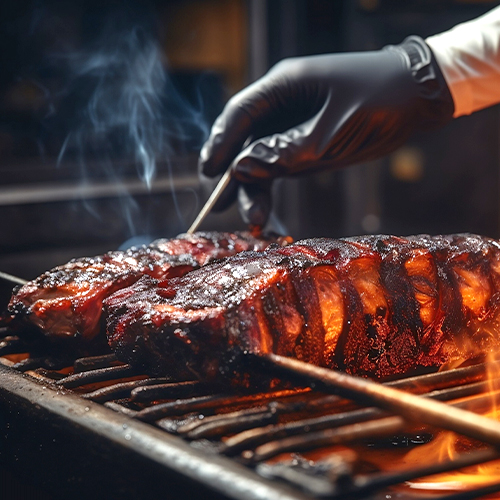

Fortunately, there's no guesswork for determining safe cooking temperatures. Food safety organizations, such as the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), set the minimum internal cooking temperatures to ensure consistency. Monitor the internal temperatures of foods you serve to prevent the spread of Salmonella, staphylococcus aureus, Listeria, and other dangerous bacteria.
Follow the recommendations below for safe cooking temperatures of common TCS foods.
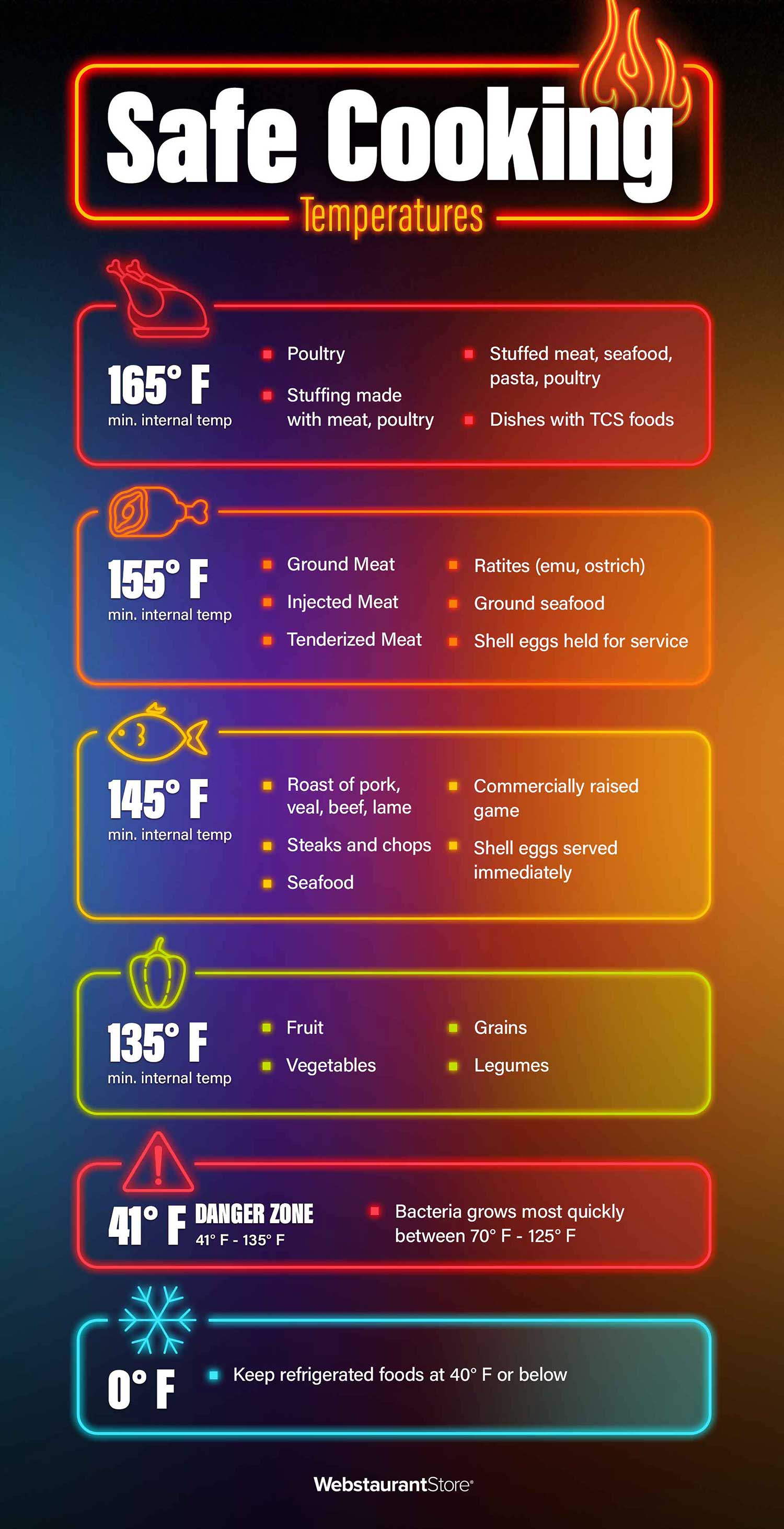
Category One: 165 Degrees Fahrenheit
Cook the following items to 165 degrees Fahrenheit for at least 15 seconds:
- Poultry, whole or ground
- Stuffing made with poultry, meat, or fish
- Stuffed pasta, meat, poultry, or seafood
- Any dish that contains cooked TCS food
Category Two: 155 Degrees Fahrenheit
Cook the following items to 155 degrees Fahrenheit for at least 15 seconds:
- Ground beef and ground pork
- Flavor-injected meats
- Tenderized meats
- Ratites (ostrich, emu)
- Ground, chopped, or minced seafood
- Eggs from the shell, held for service
Category Three: 145 Degrees Fahrenheit
Cook the following items to 145 degrees Fahrenheit for at least 15 seconds:
- Seafood, including whole lobster
- Steaks and chops (beef, pork, veal, lamb)
- Commercially raised game meat
- Eggs from the shell, served immediately
- Roasts of beef, pork, veal, lamb (must be cooked for at least 4 minutes)
Category Four: 135 Degrees Fahrenheit
Cook the following items to 135 degrees Fahrenheit for at least 15 seconds:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Rice, pasta, and other grains
- Legumes
Why Is a Minimum Internal Temperature Important While Cooking?

Maintaining a minimum internal temperature while cooking is crucial for several reasons primarily related to food safety and quality. Furthermore, proper cooking builds your establishment's reputation as a safe, tasty option for dining out.
- Food Safety: Cooking food to a specific minimum internal temperature helps prevent foodborne illnesses. Bacteria, such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter, can be present in raw or undercooked food and cause severe sickness if consumed. By cooking food to the recommended minimum internal temperature, you can effectively kill these harmful bacteria and ensure the food is safe to eat.
- Pathogen Destruction: Different foods and meats have different temperature requirements to destroy pathogens. For example, poultry and ground meats are more susceptible to contamination and require higher internal temperatures to be safe for consumption.
- Texture and Flavor: Overcooking can result in dry, tough, and less flavorful dishes, while undercooking can lead to unpalatable and potentially unsafe meals. Proper cooking temperatures can help achieve the desired texture, tenderness, and flavor.
- Quality Assurance: Meeting recommended internal temperatures is vital for quality assurance in commercial food preparation, ensuring that food products meet safety standards and customer expectations.
- Consistency: Following temperature guidelines helps ensure consistency in each dish. Food cooked unevenly is unsafe to eat even if one part meets the minimum internal temperature requirements.
- Legal Compliance: In many regions, food safety regulations and guidelines specify minimum internal temperatures for different types of foods. Failing to comply with these regulations can have legal and financial consequences for food businesses.
- Consumer Confidence: Properly cooked food reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses and builds consumer confidence. Knowing that food has been prepared safely and to the correct temperature can increase trust in restaurants and food providers.
How Long Should Meat Rest?
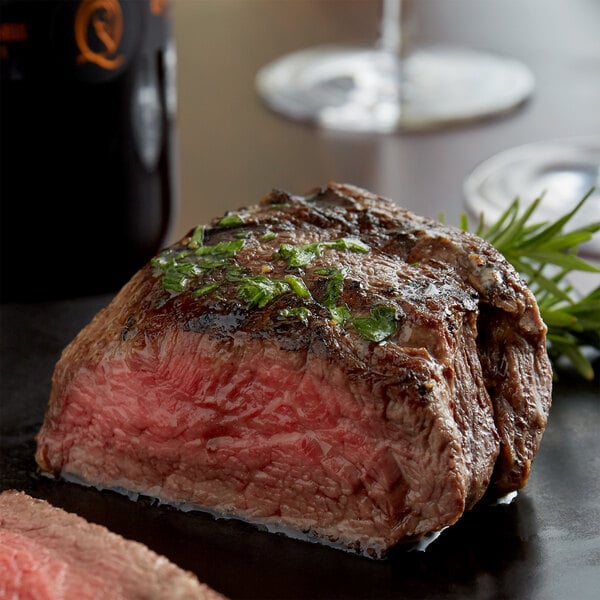

Resting meat also helps kill harmful bacteria, ensuring your food is safe for customers. Though the cooking process kills most pathogens, some bacteria may still survive in the outer layers of the steak or chicken. By allowing the meat to rest, residual heat continues penetrating the meat and eliminates any remaining bacteria.
The recommended resting time depends on the type of meat and its thickness. Below are the recommended resting times for several common items.
- Poultry: Rest poultry, such as chicken or turkey, for at least 10 to 15 minutes after cooking.
- Beef: Allow beef to rest for 5 minutes per inch of thickness.
- Pork: Similar to beef, pork should rest for approximately 5 to 10 minutes per inch of thickness.
- Fish: Rest fish for about 3 to 5 minutes after cooking.
How to Use a Food Thermometer
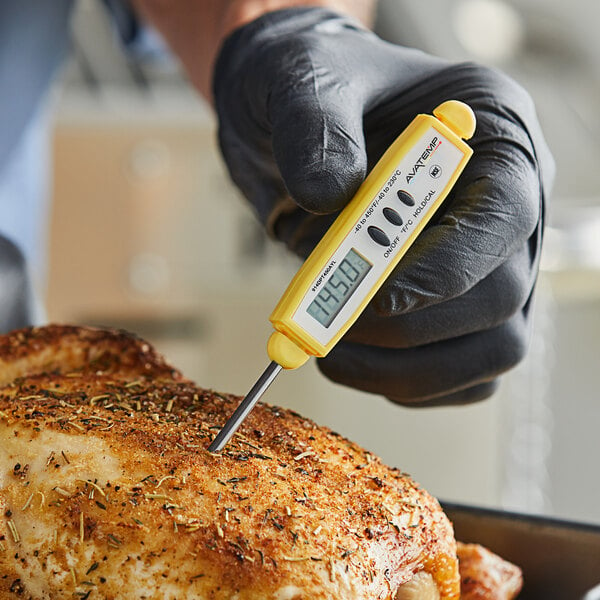

To ensure that you are cooking food safely and at the appropriate minimum internal temperature, use a food thermometer to check the temperature at different points in the dish. This tool allows you to accurately measure the internal temperature of the food, providing peace of mind that you're cooking it to a level that destroys pathogens while maintaining its quality.
- After calibrating the thermometer, insert the probe into the thickest part of the food deep enough to reach the center of the food item. For thin food items like burgers or chicken breasts, insert the probe from the side to get an accurate reading.
- Avoid touching bones or fat because they can give false temperature readings. The goal is to measure the temperature of the meat or food itself.
- Wait for the reading to stabilize. This process may take a few seconds or minutes, depending on the type and size of the food.
- Once the reading has stabilized, record the temperature displayed on the food thermometer. Compare the temperature to safe cooking temperatures and ensure it meets or exceeds the recommendation. These temperatures are guidelines provided by food safety organizations such as the FDA and USDA.
- Clean and sanitize the thermometer to prevent cross-contamination. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for cleaning and sanitizing the thermometer to maintain accuracy and store it properly.
Food Temperature Chart
Use the following food temperature chart as a guide while you cook.
By following these recommended cooking temperatures, you can safeguard against foodborne illnesses and ensure your menu items are safe for consumption. Remember to use a food thermometer to accurately measure the internal temperature of food items, as visual cues alone may not be sufficient. When cooking meat, allow it to rest for the recommended period to kill any remaining pathogens.