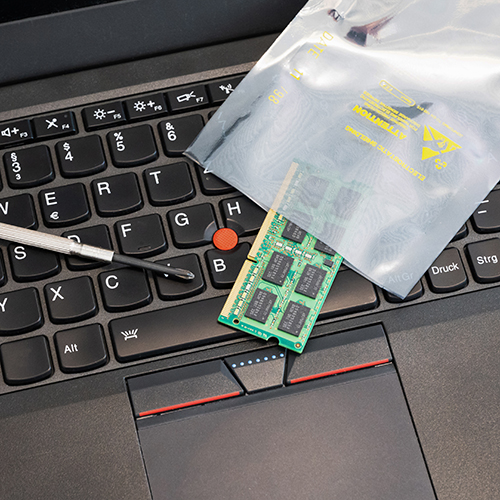
ESD stands for electrostatic discharge, which is the sudden flow of electricity between two electrically-charged objects. It occurs when there is a buildup of static electricity on one object and it comes into contact with another object or a person. ESD can damage sensitive electronic components, such as integrated circuits, transistors, and microchips. Even a small discharge of static electricity can cause latent defects or complete failure of these components.
ESD can also disrupt manufacturing processes in industries such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. It can lead to production delays, increased costs, and product defects. It can also cause personal injury to your workers, especially in environments with flammable materials. If you operate a commercial or industrial facility that works with ESD-sensitive electronics or chemicals, using ESD-safe equipment and tools is a must.
Static Dissipative vs Conductive
When protecting sensitive electronic components and equipment from electrostatic discharge, understanding the difference between static dissipative and conductive ESD equipment is crucial. Static dissipative equipment is designed to safely and slowly dissipate static charges, preventing the buildup of static electricity. This type of equipment is commonly used in environments where a low level of static electricity is acceptable, such as in cleanrooms and electronics manufacturing facilities.
On the other hand, conductive ESD equipment is specifically designed to quickly and effectively eliminate static charges, providing a high level of protection against ESD. This type of equipment is ideal for environments where a higher level of static electricity needs to be controlled, such as in explosive or flammable environments. By choosing the appropriate type of ESD equipment based on the specific setting, businesses can safeguard their valuable electronic devices and maintain optimal performance.