Coffee beans qualify as fair trade when they meet the 10 fair trade labor and sustainability standards and receive a certification from a fair trade organization. Increased global awareness and values-driven purchases have converted fair trade coffee from a coffee industry trend to an equity standard. Fair trade coffee creates transparency around where our coffee is sourced and addresses the challenges producers face in each region. Whether you operate a coffee roasting business or a cafe, learn more about the fair trade movement, how it affects the coffee industry, and where to purchase fair trade coffee so you can ethically engage in the world marketplace.
Shop Fair Trade CoffeeWhat Is Fair Trade?
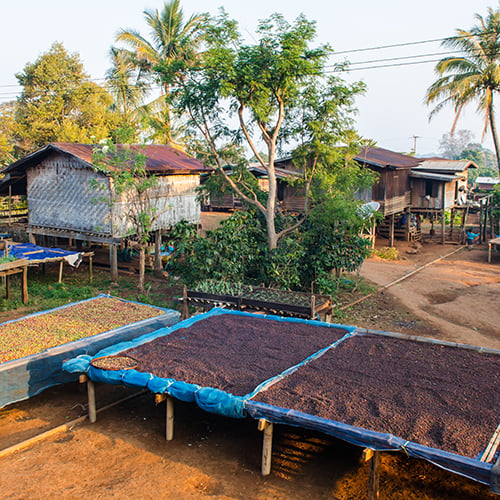

Fair trade is a movement that promotes fair pay and ethical treatment for producer groups in developing countries when they export their goods to the developed world. It is regulated by a set of standards established by non-profit, third-party fair trade associations. Fair trade certifications are awarded to companies that follow the 10 principles of fair trade.
10 Principles of Fair Trade
The World Fair Trade Organization (WFTO) prescribes the following as the 10 principles of fair trade:
- Create employment opportunities in the developing world.
- Practice transparency in communication and take accountability in actions.
- Focus on improving the lives of producers through long-term agreements and interest-free cash advances.
- Pay a fair wage to producer groups promptly and in the amount previously agreed upon by both parties.
- Prohibit the use of child labor and forced labor.
- Do not discriminate based on race, caste, ethnicity, religion, disability, gender, sexual orientation, political affiliation, HIV/AIDS status, or age.
- Maintain safe and healthy working conditions.
- Foster independence for producer groups by encouraging them to improve their internal management skills and access new markets.
- Promote fair trade by raising awareness of the issues in the developing world and how ethical trade can improve the lives of producers.
- Respect the environment by using responsible production methods.
What Does Fair Trade Mean for Coffee?
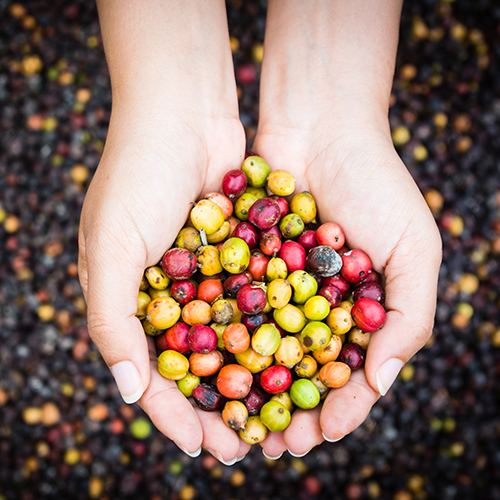

The best coffee in the world grows in a specific climate found in regions near the equator. Unfortunately, many countries where this climate exists face economic uncertainties due to governmental issues or other factors. As a result, the global price of coffee is volatile. Fair trade provides stability for farmers by offering a Fairtrade Minimum Price. There is an additional price incentive for organically grown fair trade coffee. Fair trade allows single origin coffee farmers to remain operable, producing coffee beans that showcase the flavors of their land.
How Much Do Fair Trade Coffee Farmers Get Paid?
Fair trade contracts signed as of August 1st, 2023, will have an increased baseline Fairtrade Minimum Price. Fairtrade-certified Robusta prices will increase 19% to $1.20 per pound, and Fairtrade-certified Arabica prices will rise 29% to $1.80 per pound. The additional value for organic Fairtrade Minimum Price is increasing from 30 to 40 cents per pound. The Fairtrade Minimum Price has historically been approximately 40% greater than the current coffee market price. Its increase will provide farmers with price risk management support to offset steep inflation and costs incurred by climate change adaptation.
How much each fair trade coffee farmer earns depends on their specific operation. Many farmers form cooperatives in their communities. These cooperatives can sell their products to coffee companies based in North America and Europe. Fair trade coffee companies work directly with farmers to agree on a price that will work for both parties, taking into account factors such as market value and operation expenses. Once a sustainable price is agreed on, the company will pay the farmers a portion of the order cost upfront. This helps the farmers cover their expenses until the order is complete, at which time they receive the remaining balance of their order price.
How Much Profit Do Fair Trade Coffee Farmers Make?
A common misconception is that a portion of the price a customer pays for a fair trade item goes directly to the farmer. The farmer will already have been paid in full by the time the product reaches shelves. The importance of buying fair trade commodities is that customers make it possible for fair trade organizations to continue placing orders from the developing world.
Often, coffee farmers will invest their earned profits in their communities for education, healthcare, the environment, or for improving living and working conditions. For these improvements to continue, farmers must receive consistent orders from distributors. However, distributors can only buy as much as they can sell, creating a cycle that’s driven by consumers’ choice to buy fair trade.
Back to TopCertified Fair Trade Coffee

Fair trade coffee companies must meet the standards set up by fair trade organizations. They can then apply for a fair trade certification and pay membership fees to fair trade associations. To maintain this certification, fair trade coffee brands complete an annual assessment that provides information like how many times each producer has been visited. This process ensures working conditions are up to par.
Peer reviews are also common in the certification process, meaning that competitors will assess each other and report back to their organization. That way, you can trust that a fair trade-certified company is keeping up with all 10 principles of fair trade. Once they’re certified, they can put a Fair Trade Certified™ logo on their packaging.
Fair Trade Organizations
Fair trade organizations include:
- Fairtrade International
- FLOCERT
- Fair Trade Federation
- World Fair Trade Organization
Benefits of Fair Trade Coffee
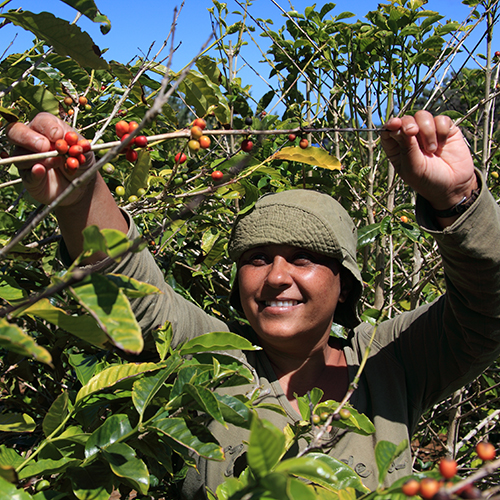

Fair trade coffee addresses many of the obstacles developing countries face. In areas where employment opportunities are scarce, people are left with no other option than to work long hours for low wages, often in unsafe conditions. Many local markets where coffee is produced are oversaturated, making the value of locally produced commodities drop substantially. Middlemen, or commodities traders, pay farmers lower prices than their goods are worth to raise their profits. As a result, farmers, their families, and their communities suffer.
Fair trade-certified coffee offers the following benefits to both you as a business owner and to local coffee growers in developing countries:
- Earn Customer Loyalty - As the public becomes more aware of problems in the developing world and the issues arising from unethical trading practices, more people are changing their purchasing decisions. Consumers have the power and want to make a positive change through the businesses they support. By offering fair trade coffee, you show your customers that you share their values and earn their loyalty.
- Long-Term Commitments - Fair trade companies commit to working with the same producer for a minimum of 3 years. Real change takes time, so long-term agreements give farmers a chance to improve their methods under the guidance of their distributors. Producers who sell their goods to a fair trade company are paid livable wages for their work, educated about human rights, and ensured safe working conditions.
- Higher Quality Coffee Beans - While the focus of fair trade is to improve the lives of people, the coffee produced under fair trade conditions is often of better quality than standard trade alternatives. This is because corners are not cut at any step of the process. For example, protecting the environment not only protects farmers against harmful chemicals but also yields a healthier coffee plant with more flavorful berries. Fair trade coffee supports farmers in the developing world and tastes better than non-fair trade coffee.
- New Markets - By selling their goods to North America and Europe, producers can get a better price because the demand is higher in those markets than at the local level.
- Eliminate Middlemen - Distributors work directly with coffee producers. This means that green coffee buyers (who purchase coffee berries before they are roasted) travel to the developing world and meet with farmers to form trading relationships built on trust and ensuring high-quality beans.
Where to Buy Fair Trade Coffee
When purchasing different kinds of coffee roasts, you should look for a fair trade-certified logo. Many companies are not strictly fair trade but still offer some fair trade products. You can often find aisles dedicated to fair trade products in grocery stores and co-ops. If you’re buying coffee in bulk online, product descriptions will mention fair trade and packages will show a Fair Trade Certified™ logo.
Fair Trade Coffee Brands
Some good fair trade coffee brands include:
- Equal Exchange
- Level Ground
- Serrv
- Pura Vida
- Higher Grounds
- Cafe Direct
- Grumpy Mule
What Is Direct Trade Coffee?
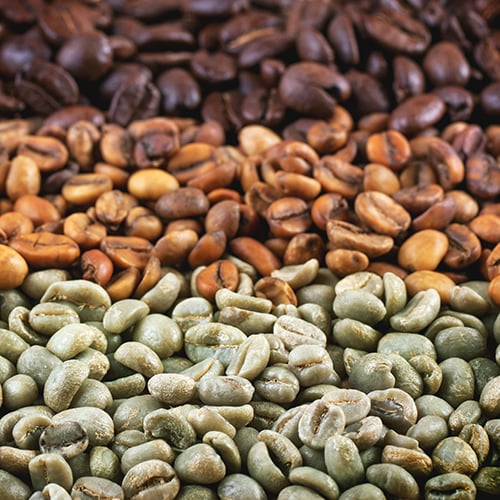

Direct trade coffee is when a roaster buys coffee directly from a producer. Direct trade coffee relies on roasters and producers establishing relationships. Together, they agree on factors like quality and pricing, resulting in lasting partnerships and higher-quality coffee beans.
Fair Trade vs Direct Trade
Fair trade and direct trade both cut out the middleman, meaning that green coffee buyers work directly with coffee farmers. Another similarity is that building a long-term buying relationship yields a better quality of coffee beans and a better quality of life for farmers. The main difference between fair trade and direct trade is their end goals. Fair trade was established to improve the lives of farmers, while direct trade places its focus on the quality of their coffee. But, just like fair trade’s social standards result in a better-quality product, direct trade’s commitment to a high-quality product ends up helping farmers.
Another difference is that while fair trade must be certified by a third-party fair trade association, direct trade does not have a legal definition and each company defines what direct trade means to them. Since there is no certification process in place for direct trade at this time, you won’t see a direct trade logo on packages. This can make it harder to distinguish true direct trade brands from brands that use the term simply for marketing purposes. So, before buying a direct trade brand, it may be a good idea to check out their website and read about their sourcing standards.
Back to TopSecond only to oil, coffee has the highest export volume to North America and Europe, allowing farmers in developing countries to sell their coffee to the developed world. It is always a good idea to research brands and companies online before buying their coffee. Not only does coffee sourcing affect working conditions for farmers and their communities, but it is also a factor in the quality and flavor of the product itself. The more you know about a brand, the more confidence you can have about providing your guests with a quality product.