Whether you're shipping from a small business or a bustling warehouse, ensuring that your products arrive safely to your customer is essential. Having the right corrugated cardboard boxes can be the key difference between a successful delivery and a disappointed customer. If your business is shipping out baked goods, prepared meals, or merchandise, choosing the right cardboard boxes can be a daunting task. Keep reading to learn about the different types of corrugated cardboard and their uses.
Shop Shipping and Receiving SuppliesWhat Is Corrugated Cardboard?
Corrugated cardboard, sometimes called corrugated fiberboard or just corrugated, is a sturdy packaging material made of three layers of kraft paper. It’s named for the interior layer of wavy paper, also called the corrugated medium, which gives the cardboard its strength. During manufacturing, the inner sheet is put through the corrugation process to create flutes or stiff folds in the paper. The corrugated medium is then glued in between two sheets of kraft paper, which form the exterior liners. Thanks to the three-layer structure, corrugated cardboard is much stronger than regular cardboard.
What Is a Corrugated Box?
Corrugated shipping boxes are made of sheets of corrugated cardboard. Stacks of corrugated fiberboard are trimmed, scored, and folded to create cartons of all shapes and sizes. Glue is applied to corners and folds for even greater stability.
Benefits of Corrugated Boxes
Sandwiched between two pieces of cardboard, the ridged flutes of corrugated paper are designed to support a great deal of weight. Not only is this beneficial for shipping purposes, but it also plays an important part in supporting the weight of food in pizza boxes and corrugated cardboard takeout boxes.
This cardboard fluting construction also plays an integral role in protecting items during transportation and preventing damages. The curved arches created by these flutes make boards durable and resist pressure applied from any angle. The empty space located between the flutes and under the arches even provides cushioning, as well as insulation in the event of extreme temperature changes.
Corrugated Flute Chart
Use our corrugated flute chart to learn the common types of corrugated board used in packaging and shipping:
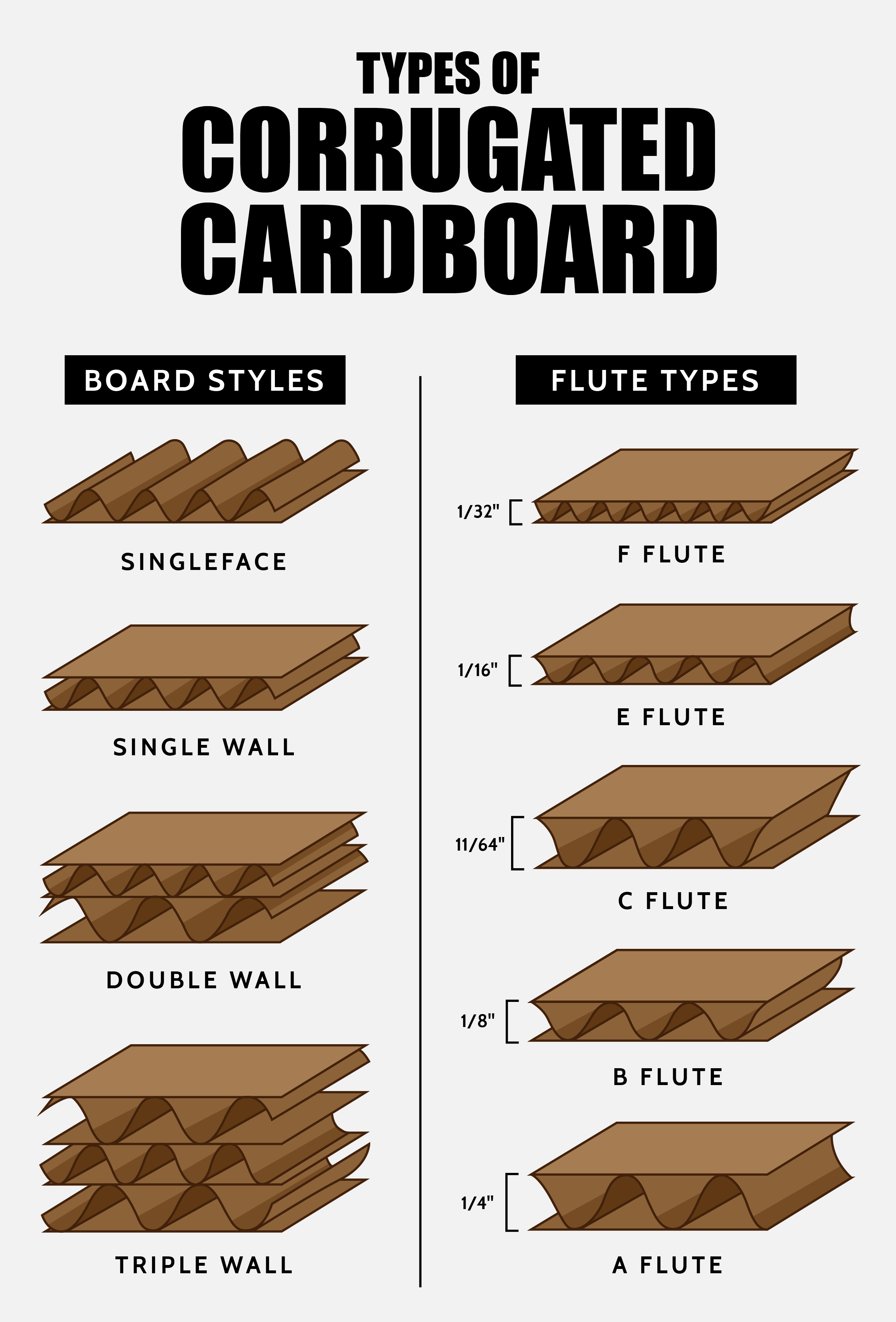
Types of Corrugated Cardboard
All corrugated cardboard has a layer of corrugated fluting and at least one liner. Fluting and liners can be combined in different layers to create different types.
Single Face Board

Single face cardboard has only two layers, a liner layer and a corrugated layer. It's not as durable as the other types of corrugated cardboard but is often used inside boxes to add extra cushioning.
- Order of Layers: Fluting, liner
- Uses: Interior packaging
Single Wall Board
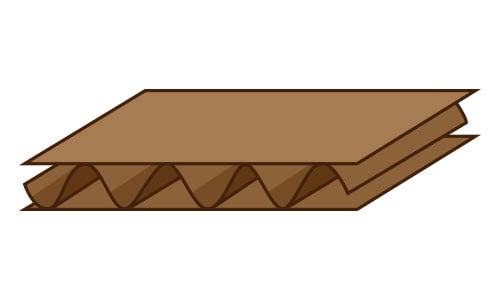
Single wall cardboard is the most common type of corrugated fiberboard. If someone is talking about corrugated cardboard, they are most likely referring to this style. It consists of two outer liners and a middle layer of corrugated medium.
- Order of Layers: Liner, fluting, liner
- Uses: Shipping cartons
Double Wall Board
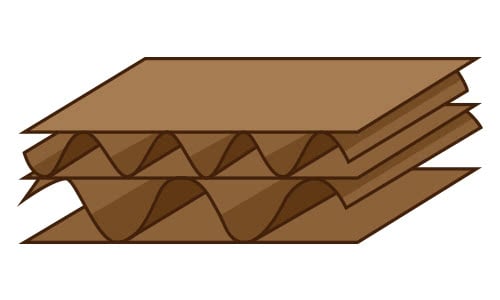
Double wall cardboard has two layers of corrugated fluting and three liners, making it extremely durable.
- Order of Layers: Liner, fluting, liner, fluting, liner
- Uses: Industrial cartons
Triple Wall Board
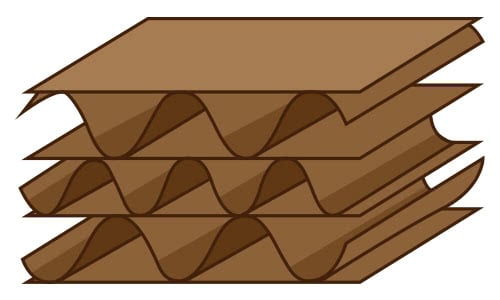
Triple wall cardboard is sturdy enough to be used in place of wooden crates. Three layers of fluting make this corrugated cardboard a dependable choice for shipping chemicals or items that need special handling.
- Order of Layers: Liner, fluting, liner, fluting, liner, fluting, liner
- Uses: Shipping crates, chemical containers
Corrugated Flute Sizes
Different types of corrugated boxes are designated by the letters A, B, C, E, or F. The most frequently used flute corrugation is C flute, with 80% of boards and boxes making up this designation. The alphabetical designations of the flutes don't correspond to the sizes of corrugated boxes, but rather to the order in which the flutes were invented.
Note: Measurements are approximations. Manufacturers produce corrugated flutes which may vary slightly in size.
A Flute Cardboard
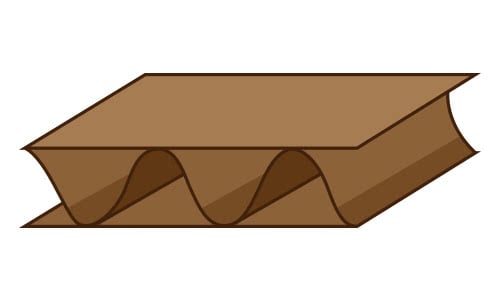
Type A cardboard has excellent compression and cushioning as well as good stacking strength. It is great for packaging and insulating fragile items, and it is commonly used to provide structural strength in boxes to protect shipments in transit.
- # of Flutes / Linear Foot: 36
- Flute Height: 1/4”
B Flute Cardboard
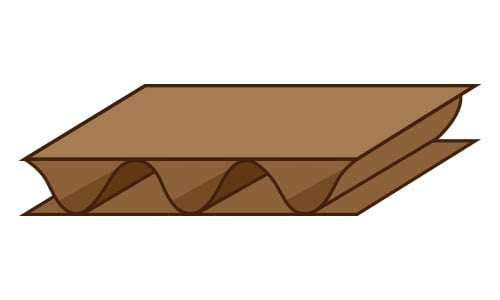
Type B cardboard has excellent crush and puncture resistance and is a great printing surface. This cardboard is commonly used for inner packaging components such as pads and partitions.
- # of Flutes / Linear Foot: 49
- Flute Height: 1/8”
A Flute vs B Flute
The difference between A flute corrugated cardboard and B flute is that B flute corrugated cardboard is half the height and features approximately 10-13 more flutes per linear foot for added strength. A flute is better for cushioning while B flute is better for stability.
C Flute Cardboard
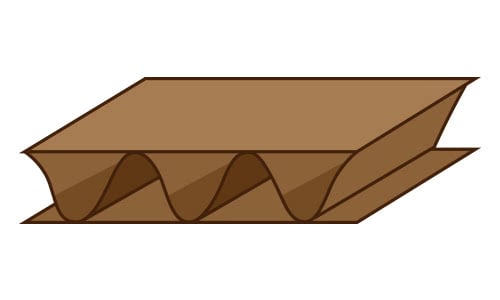
Type C cardboard makes a good printing surface. It also has compression properties and offers crush resistance. It is most commonly used for shipping boxes and to secure glass, furniture, food, etc.
- # of Flutes / Linear Foot: 41
- Flute Height: 11/64”
B Flute vs C Flute
The difference between B flute cardboard to C flute is that C flute corrugated cardboard is slightly taller and has 5-8 fewer flutes per linear foot to give it better cushioning properties to absorb impact in transit.
E Flute Cardboard
Type E cardboard’s thin construction helps to reduce storage space. It has excellent crush resistance and an exceptional printing surface. It is commonly used for displays, pizza boxes, ballot boxes, and packaging of consumer goods such as glass, ceramics, and cosmetics.
- # of Flutes / Linear Foot: 90
- Flute Height: 1/16”
B Flute vs E Flute
When comparing B flute cardboard to E flute, E flute corrugated cardboard is half the thickness with almost double the number of flutes per linear foot. Its thin construction means it takes up less space for internal packaging and allows it to fit easily through printing machines. The thickness of B flute board makes it sturdier than its thinner counterpart to support heavier items and provide additional cushioning in transit.
F Flute Cardboard
Type F cardboard has an outstanding printing surface and excellent crush resistance. Its thin construction allows for stiffer boxes with less fiber. It is commonly used in fast food clamshell containers and packaging for consumer goods such as cosmetics, jewelry, and shoes.
- # of Flutes / Linear Foot: 128
- Flute Height: 1/32”
E Flute vs F Flute
While both are exceptionally thin, F flute corrugated board is half the size of E flute and features 35-40 more flutes per linear foot than E flute cardboard. Being slightly thicker than standard paper, F flute is ideal for printing machines and easier to fold than E flute.
Corrugated Cardboard Recycling
Restaurants, grocery stores, and convenience stores accumulate corrugated cardboard with every shipment of food and supplies. Over time, the amount of cardboard quickly adds up. To dispose of the corrugated cardboard in the most efficient way, most businesses work with a local waste disposal company that collects and recycles the old corrugated containers (OCC).
To prepare the cardboard for recycling, all packing materials should be removed and the boxes must be flattened. Cardboard with grease spots cannot be recycled, so any portions of the box that have been soiled must be cut out. Tape and labels can be left in place because they are sorted out during the recycling process. For warehouses and industrial environments that produce large quantities of OCC, using a cardboard baler helps to save space.
Corrugated cardboard is the material of choice for anyone that needs to ship or package products. Now that you have an understanding of the types of corrugated fiberboard boxes and fluting sizes, you can choose the corrugated cardboard that's best for your business.