Types of Material Handling Equipment
When considering the many functions of a warehouse, tasks like loading and unloading shipments, stocking shelves, and packing and shipping goods might come to mind. Regardless of the primary job of a specific warehouse, material handling is a fundamental aspect of its operations. Therefore, warehouse operations rely heavily on material handling equipment, defined as mechanical devices that aid in moving and storing goods. There are many types of material handling equipment, each with a specific purpose, and understanding these details allows warehouses to work with optimum efficiency.
Whether you're starting a warehouse venture or looking to upgrade old equipment, our guide explains the various types of material handling equipment and their uses so you can make informed decisions.
Shop All Material Handling Equipment
Use the following links to explore different types of material handling equipment:
The term "material handling equipment" is somewhat vague, especially given a warehouse's range of tasks. Material handling refers to the safe transportation, storage, and processing of goods from the manufacturing stage to purchase. Material handling equipment allows workers to do this task efficiently with minimum strain, assisting them in moving heavy shipments with ease. This equipment is vital to every stage of warehouse operations, so having the right equipment is crucial.
There are four main categories of material handling equipment:
- Storage equipment: Equipment used to organize and store large quantities of goods
- Industrial trucks: Manually operated equipment used to transport goods across the warehouse
- Engineered systems: Automated machines designed to move goods along preset paths
- Bulk handling equipment: Equipment for managing large quantities of loose materials, such as grain or salt
Unlike the other equipment categories, storage equipment is self-explanatory. Since warehouses receive, process, and ship goods, they also need to store materials in the interim. While some items might only require short-term storage, you also want to have long-term storage options available. Some storage equipment is better suited for tools or lightweight items, while others can handle heavy-duty shipments.
Knowing the facility's capacity and primary functions will help you choose the right storage equipment for your operation. Below is a list of standard storage equipment for material handling.
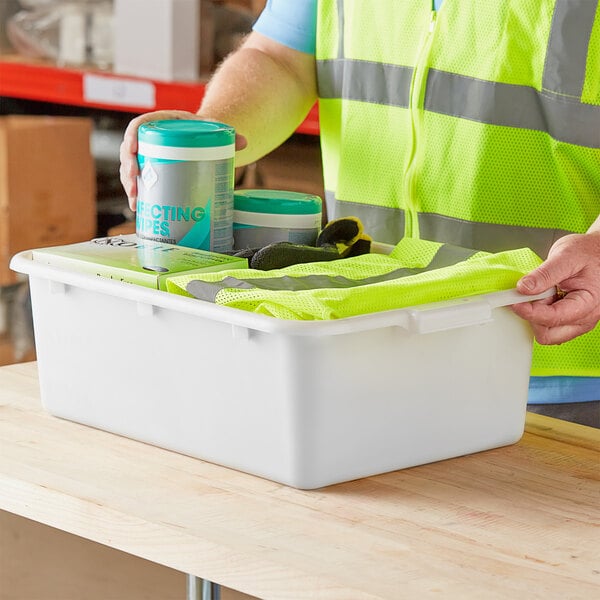

- Drawers and bins: Using drawers and storage bins for inventory and tools allows you to stay organized and keep your warehouse neat.
- Pallets: As a staple element of warehouses, pallets allow you to stack, move, and store boxes throughout your warehouse with ease.
- Shelves: A crucial aspect of warehouses are sturdy shelves to hold your small goods and supplies. When purchasing shelving units, choose options that allow you to maximize your vertical space.

- Mezzanines: A mezzanine is a portable structure that serves as an intermediate level between the floor and ceiling of your warehouse. Whether used for storage or as a work platform, implementing a mezzanine increases the efficiency of your operation.
- Racks: As a heavy-duty storage option, racks allow you to store and transport heavy loads and shipments. There are many types of racking, including pallet racks and units that include bays for forklifts to deposit shipments.
- Stacking Frames: Another way to utilize your vertical storage space is using stacking frames. This equipment includes decks and posts that support several levels of stacked pallets.
While the equipment falling under this category is diverse, industrial trucks are all used for transporting materials. Some options, such as hand trucks, are operated manually by warehouse employees. However, other pieces of equipment are fully automated. Additionally, some equipment requires specific certifications to use, such as forklifts.
There are many types of industrial trucks, but here are some of the most common ones found in industrial settings:
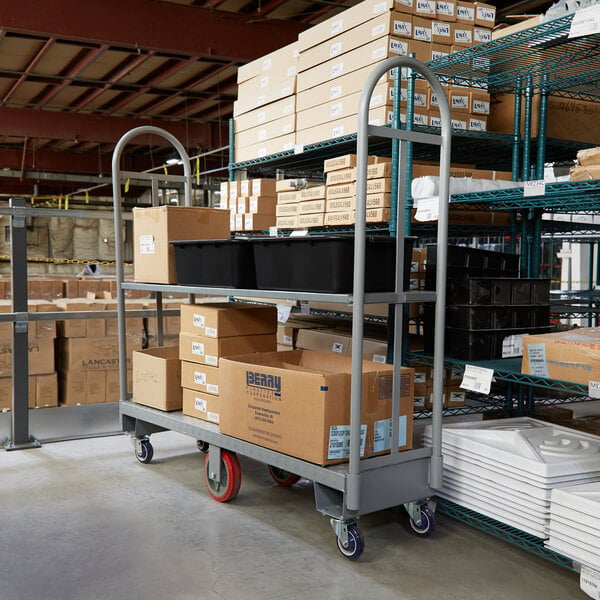

- Hand trucks: Also known as dollies, hand trucks are perhaps the most well-known piece of material handling equipment. They allow workers to wheel goods from one place to another without straining their backs.
- Sideloaders: If your warehouse has many narrow aisles where forklifts do not fit, use a sideloader to pick up or drop off items. The receivers are located on the side of the machine, allowing it to transport items through thin aisles.
- Platform trucks: A platform truck is a hand truck with a wide platform and four wheels rather than two. These features allow it to carry larger loads than its counterpart.

- Order pickers: Also known as lifts, use order pickers to safely move goods down from high shelves that are out of reach. While some only lift the operator to obtain the item, others feature a piece-part that selects the proper load automatically.
- Forklifts: Designed for transporting pallets, a forklift is the ideal equipment choice for lifting and moving heavy loads. However, they do require certification to operate.
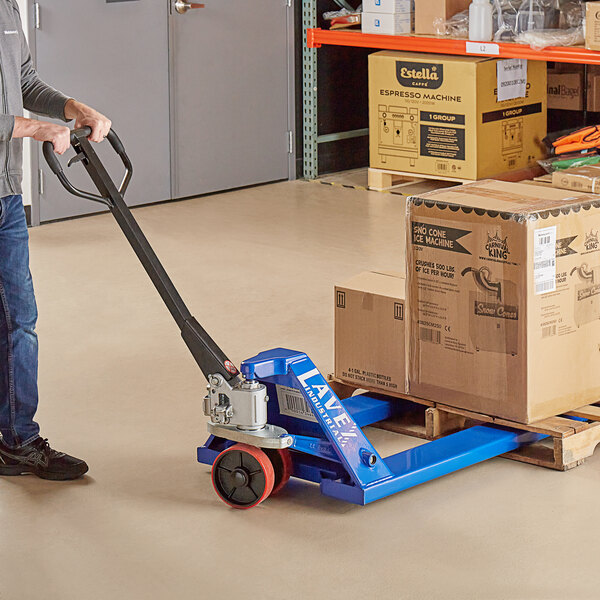
- Pallet jacks: Also called a pallet truck, a pallet jack utilizes two forks that fit into a pallet and a hydraulic pump to lift the pallet. Then, workers can push it to transport the pallet with ease.
- Walkie stackers: A walkie stacker is a forklift that workers push like a hand truck rather than drive. They can carry heavy loads with the same vertical capacity as a forklift.
Engineered systems are fully automated units that work together to perform a programmed task, such as retrieving and transporting materials from two predetermined points. Given that this equipment is a system, they often contain several machines. Engineered systems have a variety of benefits, including increasing efficiency, reducing the need for labor, and providing more protection for materials.
Below are some of the engineered systems found in many industrial establishments.
- Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS): An AS/RS unit is a computer-controlled piece of equipment that stores, handles, and retrieves materials from set points in the warehouse. In addition to AS/RS machines increasing accuracy and productivity, they also provide better product security and real-time inventory control directly connected to your network.
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs): Similar to AS/RS machines, AGVs are automated, mobile trucks that use sensors, detectors, and preset markers to transport materials and supplies throughout the warehouse facility.
- Conveyor systems: Utilizing belts, flexible chains, live rollers, and computer controls, conveyor systems move shipments through the warehouse on preset pathways. This system allows you to move large quantities of materials efficiently.
- Robotic delivery systems: Whether used in an assembly line or miscellaneous transportation, automated robotic delivery systems move materials around the facility safely and quickly.
While some assume warehouses primarily deal with pallets of carefully stacked crates, bulk material handling equipment is used for transporting, sorting, and storing loose materials. This category includes goods like salt, grain, liquids, nails, and more. There is equipment available for both vertical and horizontal transportation, as well as long-term bulk storage.
Check out some of the common bulk material handling equipment options below.

- Hoppers: There are two kinds of warehouse hoppers: dump hoppers and conical hoppers. Regardless of the type, hoppers transport and dump loose materials around the warehouse.
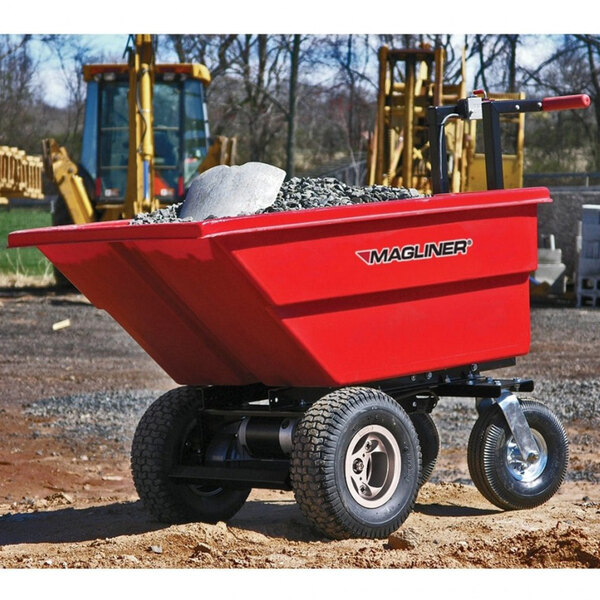
- Reclaimers: As one of the larger machines on this list, reclaimers retrieve bulk materials from storage stockpiles. Many reclaimers are now fully automated, but some still require a manual remote to operate.
- Conveyor belts: As one aspect of a conveyor system, conveyor belts rotate to move bulk materials from one location to another using drums or pulleys. This system allows workers to remain at their stations and receive necessary materials.
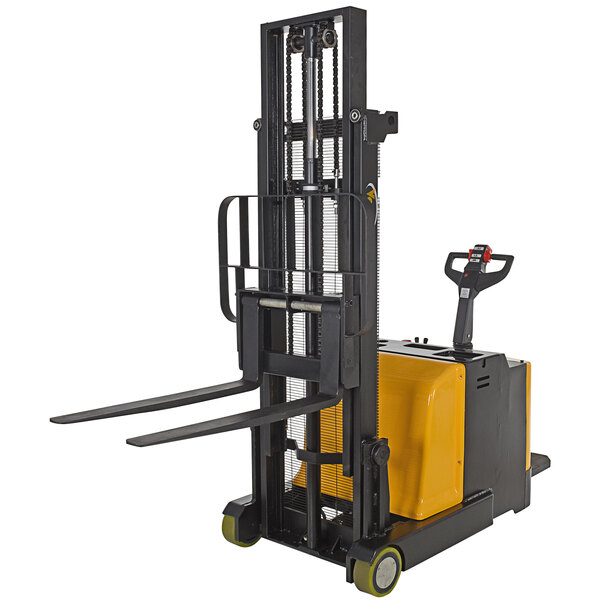

- Stackers: Similar to forklifts, stackers are automated machines that lift and stack heavy loads on docks or in warehouse storage.
- Silos: A silo is a structure designed to safely store bulk materials. The most common silos are cylindrical constructions with smooth walls and additional coatings to keep the materials fresh.
- Bucket and grain elevators: While grain elevators are designed for grain transportation, bucket elevators and grain elevators function similarly. They vertically transport bulk materials and dispense them using a unique conveyor system.
Given the importance of material handling equipment, many warehouse employees regularly work with it in their daily tasks. Warehouse owners and managers must understand the various material handling jobs, especially since some equipment requires specific operational certifications. Here are a few warehouse positions that frequently use material handling equipment:
- Warehouse workers: Given their flexible role, warehouse workers use many types of material handling equipment throughout their day. However, many will not work with heavy material handling equipment.
- Forklift operators: As the name suggests, forklift operators spend their entire day working with forklifts. This position requires training and certifications that allow them to operate heavy machinery.
- Receivers: Since they work with incoming shipments, receivers can expect to frequently work with industrial trucks, stackers, and storage equipment. They might also use material handling equipment for transportation, such as a conveyor.
- Stockers: With a primary duty of stocking and checking inventory, stockers use industrial trucks and storage equipment in their daily tasks.
- Pickers: Warehouse pickers also work closely with inventory, frequently utilizing different storage equipment and industrial trucks to transport goods. They might also operate forklifts and warehouse stackers.
- Maintenance technicians: Responsible for fixing mechanical issues in the warehouse, maintenance technicians have a working knowledge of nearly every type of material handling equipment. However, they work with engineered systems and mechanical equipment most frequently.
There are many factors to consider when selecting material handling equipment, all of which require you to know your business well. Do due diligence as you make purchasing decisions, especially for equipment as crucial to the successful operation of your warehouse as material handling equipment. Below are a few deciding factors to consider as you choose material handling equipment for your facility.
- Primary function: Understanding your business's primary tasks and materials provides valuable insight into what equipment is necessary. For example, bulk material handling equipment is less vital if you know you will not be handling loose materials.
- Personnel available: Depending on the number of employees working each shift, you need equipment that increases efficiency without becoming an additional burden. Having a small staff might mean implementing engineered systems, which would increase productivity. Additionally, check your employees' certifications to handle heavy machinery before purchasing it.
- Layout: Warehouse layout refers to the available space of your facility and the dimensions of various structures within the building. All equipment needs to be small enough to fit through doors and down aisles, so measure these features before choosing equipment. You also want to consider the vertical space of your warehouse before purchasing shelves, racks, and other equipment.
- Budget: Material handling equipment requires a significant financial commitment, so carefully consider the needs of your warehouse and available funds. For small, temporary operations, renting equipment might be a wise decision. Additionally, equipment might require inspections, operating costs like gasoline, and maintenance, which will also impact your budget.
- Operational considerations: Some warehouses work temporarily while others are permanent operations. Similarly, some facilities require managers to frequently change their layouts while others keep a specific configuration the same for long periods. For example, conveyor systems help increase efficiency for permanent operations but become a burden for temporary warehouses or facilities with a changing layout.
The safety of your employees and the goods in your warehouse are top priorities, so familiarize yourself with material handling equipment safety standards. While some equipment items require little more than common sense to operate correctly, heavy machinery and large equipment items have extensive safety guidelines. Ignoring these safety standards can lead to significant injuries and even death.
In addition to carefully following safety standards, offer safety training to all employees regarding the equipment they use most frequently. You can check out our warehouse safety measures guide for more detailed guidelines, but here are some basic safety standards for material handling equipment.
- Perform daily checks of your material handling equipment, especially heavy machinery and equipment used frequently. These checks should include visual examinations for damage and operational checks before beginning the day's tasks.
- Understand the different functions and carrying capacities of your forklifts and create a designated forklift parking area so they do not become obstacles. Utilize forklift safety best practices in all aspects of your operation.
- Write and enforce a workplace dress code for employees, which includes proper PPE, clothes that will not get caught in machinery, and bright vests to ensure visibility.
- Design a warehouse layout in a logical manner that increases workflow with clear markings and wide aisles for equipment operators. Additionally, keep floors clear of obstacles and hazards.
Related Resources

Types of Ladders
Ladders are a vital tool for simple repair jobs and everyday industrial use, allowing you to reach all corners of your establishment. However, choosing the right ladder for a job requires considering more than convenience. The wrong ladder with an incorrect duty rating or application can lead to potentially fatal accidents. Understanding the different types of ladders available and their applications, duty ratings, and features provides discernment on which ladders to use for your business or in various areas of your warehouse . Whether you're looking for a ladder for a specific use or buying an assortment of ladders to start your business, our guide on the various types of ladders on the market will help you make an informed purchase. Shop

Types of Saws
Whether you are a professional woodworker, setting up a warehouse , or running a construction company, saws are indispensable tools for achieving precise and efficient cuts in various materials. Both manual and power saws allow operators to efficiently trim and cut through wood, stone, ceramic, metal, and plastic. There are many types of saws with specific applications ranging from removing trees to tiling a bathroom, so be sure to choose the best tool for the project ahead. Shop All Power Saws Use the following links to learn more about types of saws: Jigsaw Table Saw Miter Saw Chainsaw Band Saw Scroll Saw Circular Saw Chop Saw Reciprocating Saw Pole Saw Hack Saw Tile Saw

Generator Buying Guide
Food spoils when the refrigerator won't cool, chefs can't cook when the oven won't heat, and power tools are useless when you're off the grid. Whether electrical access is unavailable or the power goes out in your building , you need a way to keep things running. That's where generators come into play.
- Topics 1346
- Industrial 55
- Troubleshooting Guides 21
- Restaurant Management 128
- Bar Management 55
- Catering Tips 35
- Bakery Management 42
- Food Trucks & Concessions 49
- Advertising & Marketing 37
- Eco-Friendly Tips 11
- Facility Layout & Design 41
- Coffee Shop Tips 28
- Installation & Maintenance 51
- Janitorial & Pest Control 30
- Safety & Sanitation 88
- Startup Tips 104
- Menu Design 10
- Kitchen & Cooking Tips 81
- Hospitality Management 23
- Pizza & Sandwich Shop Tips 36
- Smallwares 37
- Food Prep 88
- Tabletop Items 17
- Disposables 22
- Calculators & Tools 6
- Consumables 52
- Warewashing & Laundry 18
- Cooking Equipment 90
- Food Storage & Refrigeration 51
- Beverage Equipment 34
- Office Supplies 6
- Resource Type
- In-Depth Articles272
- Buying Guides296
- How-Tos93
- Product Reviews77