OSHA Regulations for Restaurants
Last updated on 7/14/2023Maintaining the health and safety of your employees while they work in your restaurant is of utmost importance in running a thriving foodservice establishment. The Occupational Safety and Health Act, commonly referred to as "OSHA," is a crucial governing body that aims to safeguard employees from workplace injuries and mistreatment. Keep reading to gain a deeper understanding of OSHA's relevance to the restaurant industry to ensure that your establishment remains compliant.
What Is OSHA?
OSHA, or the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, is a federal agency that ensures safe and healthy working conditions for employees. While OSHA primarily focuses on manufacturing and warehouse safety, it is important to note that OSHA regulations also apply to restaurants and other food service establishments.
Are Restaurants Governed by OSHA?
Yes, OSHA regulations do apply to restaurants and other food service establishments. One of the key aspects of OSHA's regulations is the requirement for employers to provide a safe and hazard-free work environment. This means that restaurants must take measures to identify and address potential safety hazards that could harm employees. For example, OSHA mandates that restaurants have proper ventilation systems in place to prevent exposure to harmful fumes and chemicals, as well as adequate lighting to reduce the risk of slips, trips, and falls.
OSHA Guidelines for Restaurants
Working in a restaurant is a physically demanding job. Foodservice employees perform many duties that can become hazardous if certain precautions are not taken by operators. Be aware of these common OSHA violations:
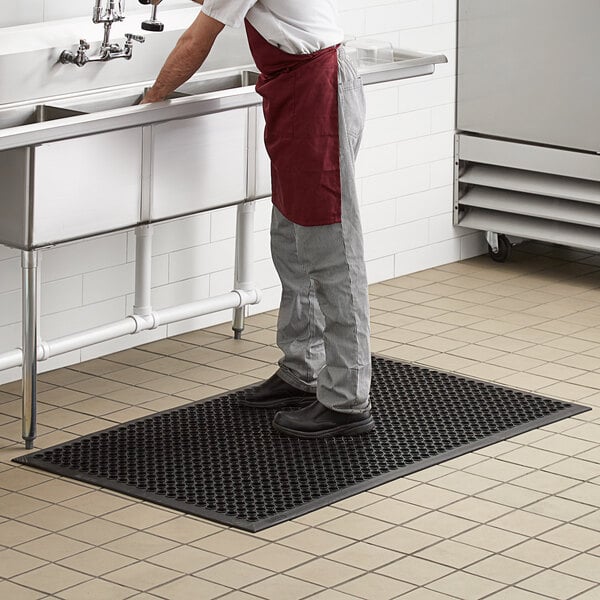

1. Slips, Trips, and Falls
Restaurant kitchens and dining areas are prone to slippery surfaces, cluttered walkways, and uneven flooring, making slips, trips, and falls a common OSHA violation. To prevent these accidents, it is essential to keep floors clean and dry, promptly address spills, ensure proper drainage, and maintain clear and unobstructed walkways. Slip-resistant footwear and the use of floor mats can reduce the risk of accidents.
2. Hazard Communication
This violation is often related to the improper labeling and handling of hazardous chemicals in the workplace. Restaurants commonly use cleaning agents, sanitizers, and other chemicals that can pose health risks if not properly managed. To comply with OSHA standards, it is crucial to have a comprehensive hazard communication program in place, including proper labeling, safety data sheets (SDS), and employee training on handling and storage procedures.
3. Fire Safety
Restaurants are at a higher risk of fire due to the presence of open flames, cooking equipment, and flammable materials. OSHA violations related to fire safety often include inadequate fire extinguisher maintenance, blocked fire exits, improper storage of flammable liquids, and lack of employee training on fire prevention and response. To comply with OSHA standards, ensure that fire extinguishers are properly maintained, fire exits are unobstructed, and employees are trained on fire safety protocols.
4. Electrical Safety
Inadequate electrical safety measures can lead to electrical shocks, fires, and other hazards in restaurants. OSHA violations in this area often include the use of damaged or frayed electrical cords, improper grounding, and overloading electrical outlets. To prevent these violations, it is essential to regularly inspect electrical equipment, repair or replace damaged cords, and ensure that outlets are not overloaded. Additionally, providing proper training to employees on electrical safety can help prevent accidents.
5. Heat Stress
Heat stress is a serious concern in commercial kitchens, especially during peak hours when the heat from cooking equipment and appliances can quickly raise the temperature. OSHA requires employers to implement measures to prevent heat-related illnesses such as heat exhaustion and heat stroke. You should provide access to cool drinking water and train employees on recognizing the signs and symptoms of heat-related illnesses.
6. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
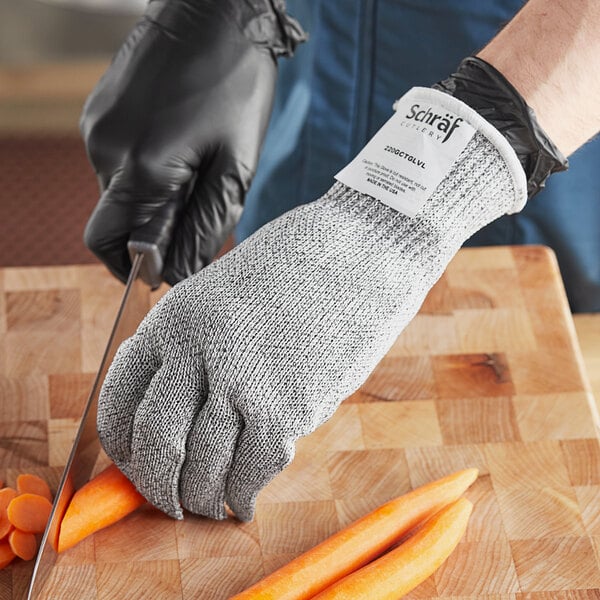

OSHA requires employers to provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to their employees when necessary to protect them from cuts and burns. Common violations in restaurants include not providing or enforcing the use of PPE such as gloves, aprons, and slip-resistant footwear. To comply with OSHA standards, assess the hazards present in your restaurant and provide the necessary PPE to your employees.
7. Lifting and Carrying
According to OSHA's guidelines, employees should be trained on proper lifting techniques, including how to assess the weight of an object, maintain a neutral spine, and use their legs and core muscles to lift rather than their back. Mechanical aids, like hand trucks and dollies, should be used whenever possible to reduce bodily strain. This can include using carts to transport heavy boxes or using lift-assist devices for items like kegs or heavy pots.
Reporting Injuries to OSHA

Another aspect of OSHA's regulations is the requirement for employers to keep accurate records of workplace injuries and illnesses. Restaurants are required to maintain injury and illness logs, known as OSHA 300 logs, which document any work-related injuries or illnesses that occur within the establishment. These records help identify trends and areas for improvement in terms of workplace safety.
In the event of an injury occurring in your restaurant, you can find the correct forms on the OSHA website. Below, we'll explore the circumstances under which reporting injuries to OSHA is required and the potential consequences of non-compliance.
- Severe Injuries - In the case of a severe injury or illness, you are required to report the incident to OSHA. Severe injuries include any work-related fatalities, hospitalizations, amputations, or loss of an eye. These incidents must be reported to OSHA within 24 hours of the occurrence. This reporting requirement applies regardless of the size of your restaurant or the number of employees.
- OSHA Recordkeeping - Even if an injury does not meet the criteria for immediate reporting, you may still need to maintain records of the incident. OSHA requires employers to keep a log of work-related injuries and illnesses using the OSHA Form 300. This log should include details such as the date of the incident, a description of the injury, the affected employee's name, and any treatment provided. These records must be maintained for five years.
- State-Specific Requirements - In addition to federal regulations, some states have their own reporting requirements for workplace injuries. These state-specific rules may have different reporting thresholds or timelines than those outlined by OSHA. Make sure to familiarize yourself with the laws in your state to ensure compliance.
- Consequences of Non-Compliance - Failure to report severe injuries to OSHA within the required timeframe can result in penalties and citations. Depending on the severity of the violation, fines can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars. Non-compliance with OSHA recordkeeping requirements can lead to citations and further penalties. These penalties not only impact your restaurant's finances but also its reputation and employee morale.
Back to Top
OSHA Restaurant Inspections

Does OSHA inspect restaurants? Yes, OSHA has the authority to conduct foodservice inspections to ensure compliance with health and safety standards. These inspections can be scheduled in advance or may even be unannounced. During the inspection, an inspector will assess different aspects of the restaurant to identify potential hazards or violations. This includes evaluating equipment, ventilation and exhaust systems, workspace layout, and safety protocols.
OSHA inspections cover more than just the physical aspects of your restaurant. Inspectors also examine your record-keeping practices and compliance with reporting requirements. If violations or hazards are found, OSHA can issue citations and penalties, which can vary in severity. In some cases, corrective measures may be required to address the hazards.
How to Handle an OSHA Inspection
During an OSHA inspection, remember to remain calm and follow certain steps to ensure a smooth process. By being prepared, you can help create a safer and more compliant work environment for your employees. Here are some key steps to take during an OSHA inspection:
- Greet the OSHA inspector professionally: When the inspector arrives at your facility, greet them politely and ask for their identification. Always verify their credentials before allowing them access to your premises.
- Designate a point of contact: Choose a knowledgeable employee to act as a point of contact during the inspection. This person should be familiar with your safety procedures and be able to provide the inspector with any necessary documentation or information.
- Accompany the inspector: It is recommended that you or your designated point of contact accompany the inspector throughout the inspection. This allows you to answer any questions and address any concerns in real time.
- Take notes and document the inspection: Keep a record of the inspector's findings, including any violations or areas of concern. This documentation will be useful for addressing any issues and implementing corrective actions.
- Cooperate and provide requested documents: OSHA inspectors have the authority to request certain documents, such as safety policies, training records, or injury logs. Cooperate fully and provide the requested information promptly. This will help demonstrate your commitment to safety compliance.
- Correct any identified hazards: If the inspector identifies any hazards or violations during the inspection, take immediate action to address them. This may involve implementing new safety procedures, providing additional training, or repairing equipment.
- Request a closing conference: After the inspection, request a closing conference with the inspector. This provides an opportunity to discuss the findings, ask questions, and gain a better understanding of any required corrective actions.
- Follow up on any citations: If the inspector issues citations or penalties, it is important to address them promptly. Review the citations carefully, determine the necessary corrective actions, and implement them within the given timeframe.
OSHA Employer Obligations

As an employer, you must be aware of the protections OSHA offers your employees. To stay compliant with the Act's rules and regulations, make sure to do the following:
- Provide employees with a workplace that's free from OSHA-recognized hazards.
- Communicate your business's operating procedures, so that employees can understand health and safety requirements.
- Post a government-issued OSHA poster that informs employees of their responsibilities and rights in a noticeable location, such as your cafeteria or break room.
- Maintain detailed records of workplace injuries and illnesses, and make sure employee medical records are accessible to employees or their representatives.
- Consider joining an injury and illness prevention program, which is designed to help you and your employees reduce the number of workplace injuries. In turn, this could help keep everyone healthy and reduce medical expenses for both employers and employees.
OSHA Employee Protections
Employees are offered certain protections under OSHA. If workers believe their rights have been violated, two types of complaints can be filed:
Safety and health complaints are filed by employees who believe their working conditions are unsafe or detrimental to their health. Before filing, workers should try to bring the issue to their employer’s attention in an attempt to correct the problem without involving OSHA. If this isn’t possible, employees can file a confidential report with OSHA to request an inspection of their workplace.
Protection from retaliation complaints (also known as whistleblower complaints) can be filed by employees who believe they've been retaliated against for submitting a complaint to OSHA. It's illegal for any business to demote, transfer, or fire employees who exercise their OSHA rights.
OSHA Restaurant FAQ

If you still have questions about OSHA kitchen safety, check out the FAQ section below.
When Was OSHA Founded?
The Occupational Safety and Health Act was signed by Congress and then-President Richard Nixon on December 29, 1970. OSHA was officially formed as a government agency on April 28, 1971. The organization is part of the United States Department of Labor, and the program's administrator is the Assistant Secretary of Labor for Occupational Safety and Health. OSHA's administrator reports to the Secretary of Labor, who is a member of the cabinet of the President of the United States.
What Is the Main Purpose of OSHA?
The main goal behind OSHA is to establish that a safe workplace is a basic human right and that no worker should have to choose between their life and their job. Accordingly, OSHA sets and enforces safety standards while also providing employers and employees with outreach, assistance, education, and training.
Does OSHA Cover Meal Breaks?
It's a common misconception that OSHA requires meal breaks. Currently, there is no specific OSHA regulation that governs meal breaks for adults over 18, but it's expected that employers provide reasonable break times for employees. Some states require employers to provide a specific duration and frequency of meal breaks, while others may not have any specific requirements at all. Employers should familiarize themselves with both federal and state regulations to ensure compliance.
Does OSHA Regulate Child Labor?
OSHA is responsible for ensuring the safety of all workers regardless of age, but they do not set or regulate child labor laws. In the US, the primary agency responsible for regulating child labor is the Department of Labor (DOL). Under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), the DOL sets guidelines and standards for the employment of minors.
Back to Top
OSHA plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of employees in many industries, including the restaurant sector. As a restaurant owner or manager, it is essential to be aware of the common OSHA violations that can occur in your establishment. Implementing preventive measures, conducting regular inspections, and providing proper training to your staff can help you maintain OSHA compliance and create a safe working environment for everyone.