Types of Beef Cuts
Beef is a popular ingredient in nearly every world cuisine, and it's easy to see why. From premium Argentinian asado to convenient fast food burgers, there is an endless number of uses for beef to suit any occasion. Learn how to differentiate between the different cuts and varieties so you can offer guests the perfect piece of beef at your butcher shop or your next event.
Shop All Wholesale Beef
Use the following links to explore the types of beef cuts out there, so you can make more informed purchases for your menu!
What Are the Cuts of Beef?
A steer is divided into 8 main regions, which are called primal cuts. From there, the primal cuts are divided into subprimal cuts for foodservice and can then be further broken down into portion cuts, or retail cuts.
Primal Cuts of Beef

There are 8 main primal cuts of beef: chuck, rib, loin (consisting of the short loin and the sirloin), round, flank, plate, brisket, and shank. Divided by groups of muscles, the meat from each primal has its own unique flavor, texture, and level of fat and marbling due to how hard the muscles were worked.
Subprimal Cuts of Beef
Primals are cut and divided into subprimals, also known as "foodservice cuts." These large cuts are often purchased by restaurants in order to save money over buying individual steaks and to allow chefs to have full control over how their meat is cut and trimmed. Subprimals are further trimmed down into portion cuts, such as steaks, roasts, and ribs, which typically appear in grocery stores and on restaurant menus.
Best Cuts of Beef
The most tender cuts of beef come from the primals that are located farthest from the head and hooves, towards the center of the cow. These are some of the least hard-working muscles on the animal, so they lack dense connective tissue. On the other hand, the primals that make up the legs and rump of the cow are not as tender but offer a rich, beefy flavor. These strong muscles work hard during the animal's lifetime, developing rich fat marbling throughout the meat and a good deal of connective tissue.
Different Types of Beef
Check out our list of the different beef primal cuts to learn more about which subprimal and portion cuts come from each and the best cooking methods to use.
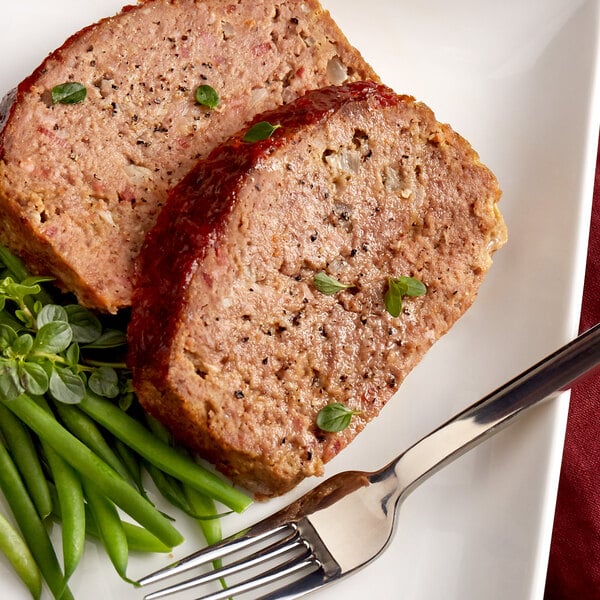

The chuck primal consists of the shoulder and neck region of the cow. Due to its high amount of connective tissue and fat content, chuck beef cuts are tough, yet flavorful, and benefit from low and slow cooking methods to tenderize the meat. Ground beef is most commonly sourced from the chuck primal.
Chuck subprimal cuts: Chuck roll, shoulder clod, chuck tender, square chuck
Popular chuck portion cuts: Chuck shoulder roast, flat-iron steak, chuck short ribs, Denver steak, stew meat, and ground chuck
How to cook beef chuck: Braise, roast, stew, grill
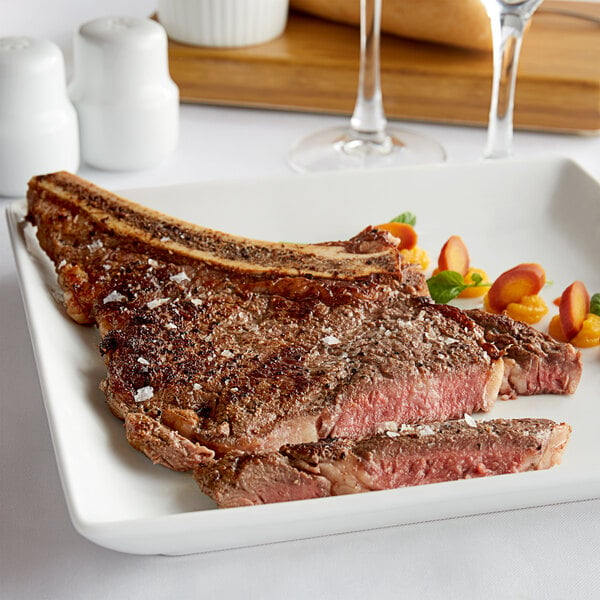

The rib primal consists of the top part of the center section of rib, specifically the sixth through the twelfth ribs of the cow. Featuring a rich, juicy flavor, beef cuts from the rib are some of the most tender cuts on the cow and can be cooked in a variety of ways.
Rib subprimal cuts: Ribeye roll, ribeye subprimal, 7-bone rib
Popular rib portion cuts: Ribeye steak, prime rib, ribeye filet, cowboy steak, back ribs, short ribs
How to cook beef ribs: Smoke, roast, braise, grill, broil
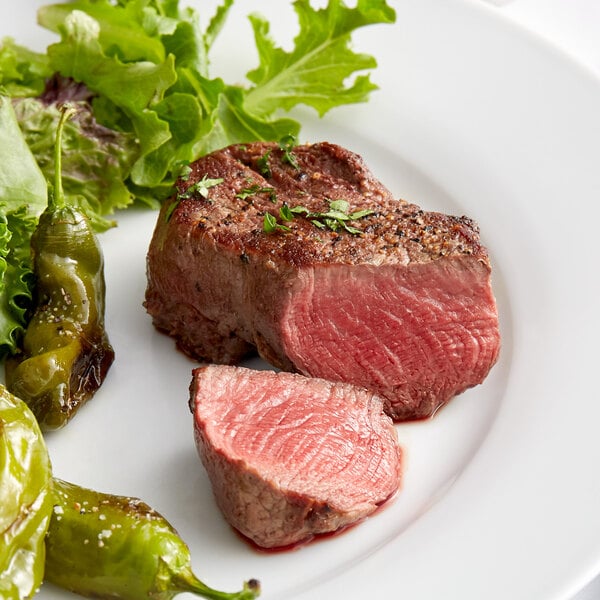

The loin primal is located behind the ribs and it is not a heavily used muscle, which makes for some of the most tender meat on the cow. Because of its tenderness, the loin is where some of the most desirable, and expensive, beef cuts can be found, such as T-bone steak and porterhouse steak from the short loin and filet mignon from the tenderloin. Beef cuts from the loin primal dry out fast when cooking, so they are typically best for quick, high-heat cooking methods to preserve their prized flavor.
Loin subprimal cuts: Tenderloin, strip loin, short loin, top sirloin, bottom sirloin
Popular loin portion cuts: Filet mignon, porterhouse steak, T-bone steak, tri-tip roast, New York strip steak
How to cook beef loin: Grill, broil, pan-sear
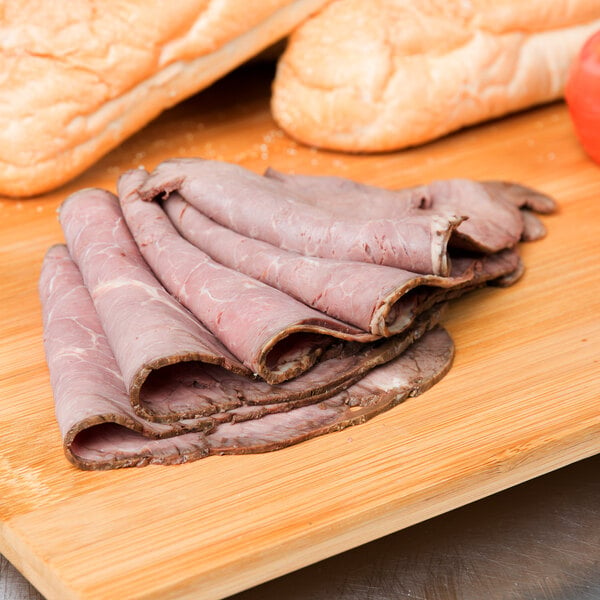

The round primal consists of beef cuts that come from the rump, hips, hind legs, and knees of the cow. Because it is made up of hard-working muscles that contain a lot of connective tissue and a lower fat content, round primal beef cuts are tougher and less expensive cuts of beef. When cooked properly, these beef cuts can be tender and have a delicious, beefy flavor. For best results, slow-cook or marinate before high-heat cooking to tenderize. The most common use for a round roast is to make roast beef for sandwiches.
Round subprimal cuts: Bottom round, top round, eye of round, sirloin tip
Popular round portion cuts: Rump roast, top round steak, eye of round steak, top round
How to cook beef round: Braise, roast, grill, pan sear
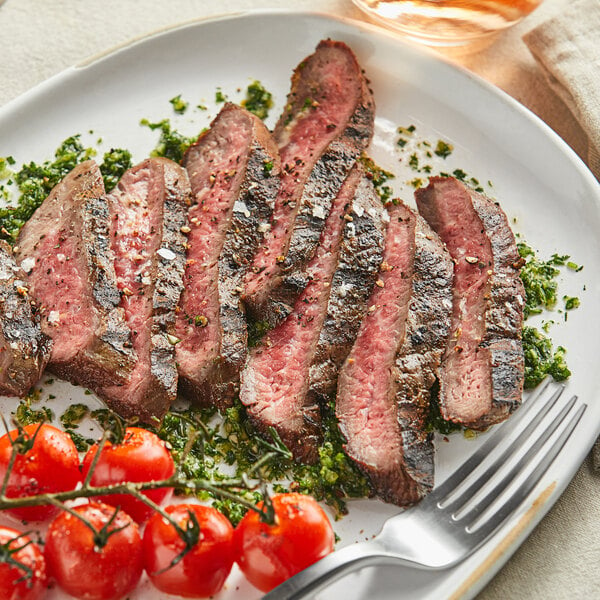

Located below the loin, the flank primal produces one cut of beef: flank steak. It is a tough and lean yet flavorful section of the cow that works best when marinated before grilling at high heat. It is also often used to make ground beef.
How to cook beef flank: Grill, broil, braise
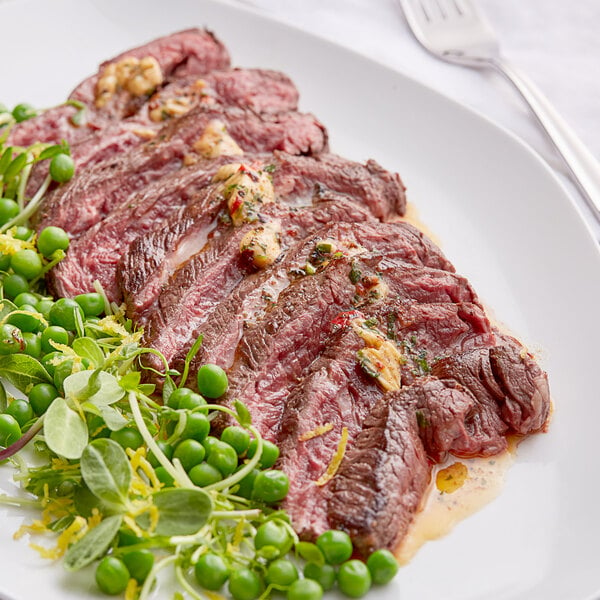

Located near the stomach on the diaphragm, plate primal beef cuts are fairly tough and fatty. Many beef cuts from the plate primal are best for fast, high-heat cooking, like skirt steak and hanger steak, while some cuts are better for braising, like short ribs.
Plate subprimal cuts: Hanger steak, inside skirt steak, outside skirt steak, plate short ribs, Franken short ribs
Popular plate portion cuts: Short ribs, ground beef, skirt steak, bacon
How to cook beef plate: Grill, pan-sear, broil, braise
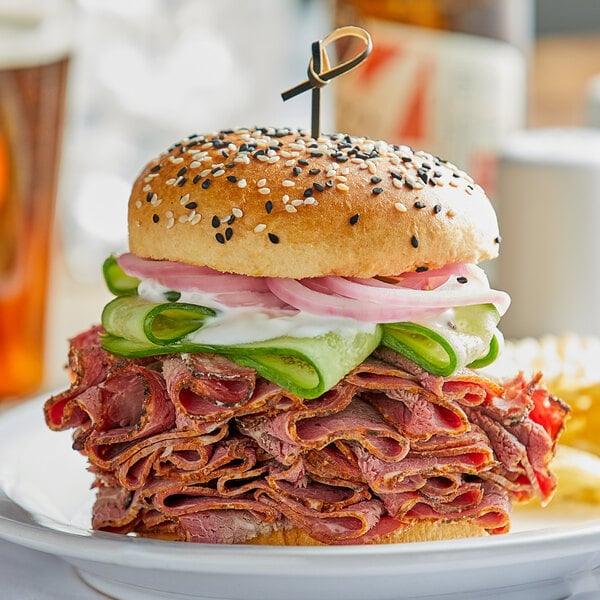

The brisket primal cut consists of the cow’s breast. Because brisket comes from a well-worked muscle of the cow, it benefits from marinating and low and slow cooking methods to achieve the melt-in-your-mouth texture and rich, beefy flavor that makes it so popular for barbecue. In addition to traditional smoked brisket and burnt ends for barbecue, brisket is also the traditional beef cut to use for corned beef.
Brisket subprimal cuts: Brisket flat half, brisket point half
How to cook beef brisket: Braise, smoke, sous vide, roast
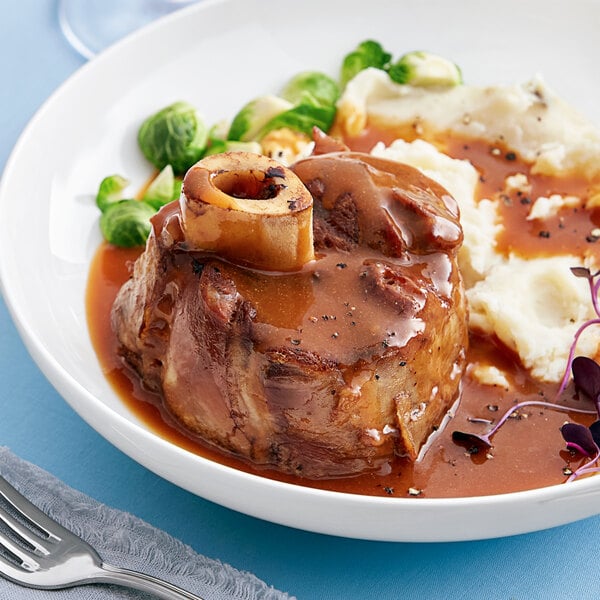

The shank primal, which consists of the cow’s forearms, produces two beef cuts: shank cross-cut and shank center-cut. Known for their tough, sinewy texture, shank is not a popular cut of meat, nor is found at many retail stores. Braised shank can give way to very tender meat, and is most popularly used for the Italian Osso Buco dish. Shank is also commonly used for ground beef and stew meat.
Shank subprimal cuts: Shank cross-cut, shank center-cut
How to cook beef shank: Braise, stew
Read on to learn the answers to some frequently asked questions about beef cuts.
What Is the Leanest Cut of Beef?
The leanest cut of beef is the eye round roast, which is located in the round primal. All cuts of beef from the round primal are incredibly lean due to their location on the cow.
What Part of the Cow is Brisket?
Brisket is located on the breast area, or lower chest portion, of the cow.
What Are the Cheapest Cuts of Beef?
The cheapest cuts of beef will come from the round primal. This includes top round steak, also known as london broil, sirloin tip steak, top round roast, eye of round steak, and eye of round roast.
How Many Steaks in a Cow?
You can yield approximately 120 to 180 cuts of steaks per the average 1200 lb. to 1400 lb. cow.
How Many Ribs Does a Cow Have?
Cows have 13 pairs of ribs for a total of 26 ribs. The first 5 pairs of ribs belong to the chuck primal and the last 6 pairs of ribs belong to the rib primal.
What Are the Primal Cuts of Beef?
The 8 primal cuts of beef are chuck, rib, loin, round, flank, plate, brisket, and shank.
Use the beef cuts diagram below as a guide to the type of beef primals and which portion cuts come from each primal. Use our printable beef cuts chart for your convenience.

Related Resources

Steak Doneness Guide
Serving steak at your guests' requested steak temperature is an essential trick of the trade. A steak that is not done well enough or is overly cooked can irk guests and result in food waste. Learn how to serve a perfect steak every time by mastering the different steak doneness levels. Follow our printable steak temperature chart to guide you in preparing steak to your guests' liking. Steak Temperature Guide For precise information about every steak temperature level, see our steak doneness guide below. No matter the steak temperature, it's always essential to follow safety temperatures and best practices, like keeping food out of the temperature danger zone. Extra Rare or "Blue" Steak Seared outside Completely red interior Cold and soft c

Best Cuts of Steak
You may know that filet mignon, prime rib, and porterhouse steaks are excellent cuts of meat, but maybe you're not sure what distinguishes them from each other. Our guide to the best cuts of steak explains what sets each steak apart so you can choose the best cuts for your preparation method. Once you understand what the best cuts of steak are, acquaint yourself with the different grades of beef to select the best quality meat. Best Cuts of Steak in Order Discover the top 10 best cuts of steak. We've arranged them in order of quality so you can see what the top contenders are while picking what works best for your menu and target clientele. 1. Filet Mignon Filet mignon is considered one of the most luxurious and expensive cuts of beef prize

Resting Meat: Why You Should and for How Long
If you're grilling the best cuts of steak , you want to make sure these premium cuts shine. Letting meat rest is an essential part of the cooking process to serve quality meat. This is true for chicken, lamb, pork, game meats , and even some fish. We explain exactly why and how long meat needs to rest so your menu has customers coming back for more. How to Rest a Steak Check out our video to learn how to rest a steak the proper way: How Long to Let Meat Rest As a general rule, rest thinner cuts of meat for a minimum of 5-7 minutes. Thick cuts should rest for 10-20 minutes before you cut into them. Meat Resting Times and Temperature The goal with steak is for the center to be between 120-130 degrees Fahrenheit and the exterior between 125-14
- Topics 1356
- Industrial 55
- Troubleshooting Guides 21
- Restaurant Management 128
- Bar Management 56
- Catering Tips 36
- Bakery Management 42
- Food Trucks & Concessions 49
- Advertising & Marketing 37
- Eco-Friendly Tips 11
- Facility Layout & Design 42
- Coffee Shop Tips 28
- Installation & Maintenance 51
- Janitorial & Pest Control 30
- Safety & Sanitation 88
- Startup Tips 104
- Menu Design 10
- Kitchen & Cooking Tips 83
- Hospitality Management 24
- Pizza & Sandwich Shop Tips 36
- Smallwares 37
- Food Prep 89
- Tabletop Items 17
- Disposables 22
- Calculators & Tools 6
- Consumables 52
- Warewashing & Laundry 19
- Cooking Equipment 91
- Food Storage & Refrigeration 51
- Beverage Equipment 35
- Office Supplies 6
- Resource Type
- In-Depth Articles272
- Buying Guides298
- How-Tos95
- Product Reviews78